Overview
Credentials provide a centralized method to provide users access to external systems, such as cloud providers. When applying a policy that needs to communicate with external APIs, users are able to select which Credential to use to authorize to the external API. Sufficiently privileged users can add new credentials, rotate credential information, and remove credentials.
Credentials are scoped to a Account within Flexera - they are created in a Account and can only be used by policies applied in that Account.
Credentials contain only the key material used to authenticate to an API - the other details of the API, including the URL, tenant information, etc, are specified in the policy template itself or provided as inputs when a policy is applied.
Getting Started
Many different users are permitted to view Credentials (the non-sensitive information only), but to manage credentials you must have either:
enterprise_manageron the Organization, oradminon the Account
Generally speaking, to authenticate against an external API, you need to use the 3rd-party system to set up an authentication principal that can be used by Flexera when making API calls. Different systems use different types of authentication methods, the most common of which are supported by credentials. For some providers, Flexera provides a provider-specific credential type to simplify the configuration process.
Generic Credential Types
- API Key
- Basic Auth (username/password)
- NTLM
- OAuth2
Provider-specific Credential Types
If you would like additional credential types supported, please let us know.
How Credentials are Used
For policies that reach out to external systems to gather information or take actions, the policy author should use credentials for authenticated API calls. When such a policy is applied by a policy manager, they will select which credential in the current account to use when the policy runs.
By default, the credential selector shows only those credentials that match the credential provider specified in the policy template. The user can press the View all credentials link to instead show all credentials in the system that match the schemes defined in the policy template.
Multi-tenant credentials
Depending on the design of the policy and the type of credential being used, a policy may interact with more than one service account/tenant/subscription/project. For example, when any Flexera-built policy for Azure and Google is applied, it iterates through all available subscriptions/projects that the credential has access to.
Therefore, when creating the credentials in the provider system, remember that when you register that credential in Flexera, any account that has that credential will run policies against all the tenants it has access to. The following diagram illustrates this behavior using Azure as an example. Note that this scenario is not possible with AWS as a separate credential is needed for each AWS account -- this is a limitation of how AWS has designed cross-account roles.
In the following example:
- Policy Alpha will run against all 5 subscriptions
- Policy Beta will run against only the 1 subscription
- Users in Project 3 will have the choice to use either credential when applying a policy. In this example, Policy Charlie will run against 2 subscriptions
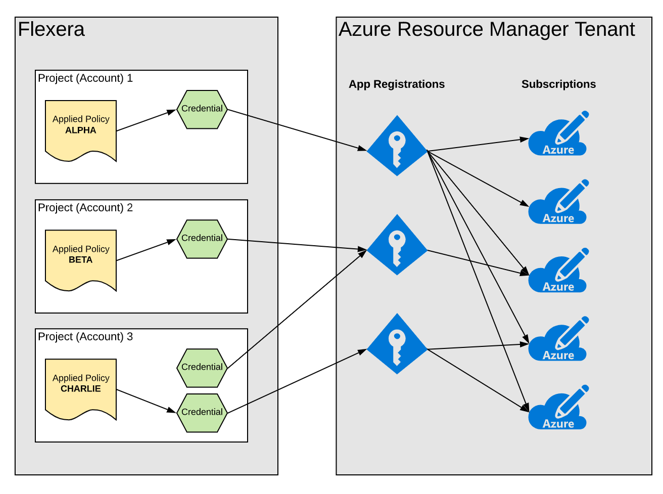
Note that this multi-tenant behavior depends on the design/code of the policy template itself. All Flexera-built policies contain code to identify all tenants the credential has access to and run the policy against each. To replicate this behavior, inspect and replicate the code of a Flexera-built policy.
Matching credentials to policies
In order to simplify the user experience around applying policies, the system provides a mechanism to match
credentials in the system with the credential-selector when applying a policy. The match is performed by inspecting the tags in the policy template credential declaration
Managing Credentials
To view and manage the credentials available in this account, select the Credentials menu on the left-hand nav of Policy Manager. Use the account selector at the top of the page to select which account you are looking at -- remember that credentials are scoped to a account, so only exist and can be used within the selected account. Your existing credentials are shown in the list. Selecting a credential will show all of the non-sensitive information about the credential, including when it was created and last updated.
Credentials can also be managed via the Credential Management API.
Creating
To create a new credential, press the New Credential button -- a slideout will appear with all of the configuration options for the credential. The first field allows you to select which type of credential to create. Depending on what's selected, different fields will be available. There is a common set of inputs for all credential types as follows:
Credential Name- User-friendly name for the credential. This name will show in the Credentials page list and in the list of available credentials when applying a policy.Credential Identifier- The unique ID for this credential in this account that is used to identify the credential in API calls. This value is auto-generated from the name, or can be tailored as you see fit. Once a credential is created, its identifier can not be changed.Credential Description- Brief description of the credential that is shown on the Credentials page.Provider- A free-text field that is used to match this credential with credentials specified in policy templates when using generic credential types. For more details see how credentials map to policies.
For details on how to connect credentials for various services, see the Generic Credentials and Provider-Specific Credentials sections below.
When creating a new credential using the API, use the PUT call for the specific credential type that you are trying to create and the ID of the call you make becomes the credential identifier. A list of all available API credential types can be found in the API docs.
Updating and Rotating
To update any part of a credential, including the key material, navigate to the Credentials page, select the correct account, select the credential, and press the Edit button in the lower-right corner. Once a credential is updated, any policy using that credential will use the new information the next time it is evaluated.
When updating a credential using the API, use the PATCH call for the credential you are modifying and provide any fields that require updating.
Removing
To remove a credential, navigate to the Credentials page, select the correct account, select the credential in the list, and press the Remove button in the lower-left of the page. When a credential is removed, any policy that uses that credential will fail evaluation from that point forward. Such policies need to be re-applied with a new credential to continue functioning.
When removing a credential using the API, use the DELETE call with the path of the credential you are removing.
Generic Credentials
The generic credentials can be used to authenticate with most API services, and the specific format and content of the fields are driven by what the service requires. The following sections describe each generic credential type and how they might be used.
API Key
Used for services that have a simple API key that is used to authenticate. Generally this is just a string that is provided with some guidance on how to use that string in an API call. Some systems require the key be sent in a header while others require the key is sent in the query string.
Details for creating an API Key credential using the API can be found in the API docs using the scheme api_key.
Basic Auth (Username/password)
Used for services that use username/password authentication.
Details for creating a basic auth credential using the API can be found in the API docs using the scheme basic.
JWT (JSON Web Token)
Used for services that require JSON Web Tokens, which follow an industry standard for authentication between two parties.
This type is only available using the API using the jwt scheme.
NTLM
Used for services that leverage NTLM authentication, which generally speaking is Windows-based services. If the auth requires domain and username, use the domain\username format in the username field.
Details for creating an NTLM credential using the API can be found in the API docs using the scheme ntlm.
OAuth2
Many web services support OAuth2 for authentication. OAuth2 comes in many flavors with different grant types, such as client credentials, JWT bearer, and refresh tokens. The configuration page supports all those types of OAuth2 credentials and the various options for each.
Details for creating an OAuth2 credential using the API can be found in the API docs using the scheme oauth2.
Provider-Specific Credentials
AWS
Flexera supports multiple authentication types for AWS, with Cross-Account Roles being the preferred method per AWS best pratices.
No matter which method you use, you will need to ensure that the AWS IAM Role (or user) has enough permissions to successfully evaluate the policy and take remediation actions (if so desired). All Flexera-built policies contain the required permissions in their readme.
Security Token Service (STS) Cross-Account Roles
The preferred method for connecting to AWS, cross-account roles provide a method for you to grant Flexera access to your account in a defined and constrained way.
In Flexera Governance, navigate to the Credentials page, press the New Credential button, and select the AWS Security Token Service (STS) Cross-Account Role credential type.
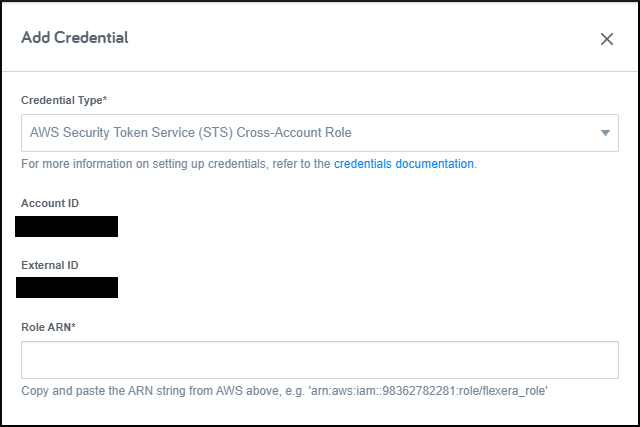
To create a cross-account role in AWS, follow the AWS instructions.
- During the role creation process in AWS, be sure to select
Require external ID
option. - In AWS you will need to enter the
Account IDand theExternal ID-- both of these values are shown in the Credentials page once you've selected the STS credential type. - Specify which AWS permission policies are attached to the role based on the Flexera policies that you will be using.
Once the role has been created in AWS, select it and copy the Role ARN value to enter into the Flexera credentials screen in the Role ARN field.
API Usage
Details for creating an AWS STS credential using the API can be found in the API docs using the scheme aws_sts.
The standard provider name to match credentials in Flexera-built policies for AWS is: aws
Key rotation
This type of credential does not need to have keys rotated.
AWS IAM User
Per AWS best practices, strongly consider using the Cross-Account role method documented above instead of an IAM user. If you still wish to use an IAM user, follow the instructions below.
In Flexera Governance, navigate to the Credentials page, press the New Credential button, and select the AWS IAM User credential type.
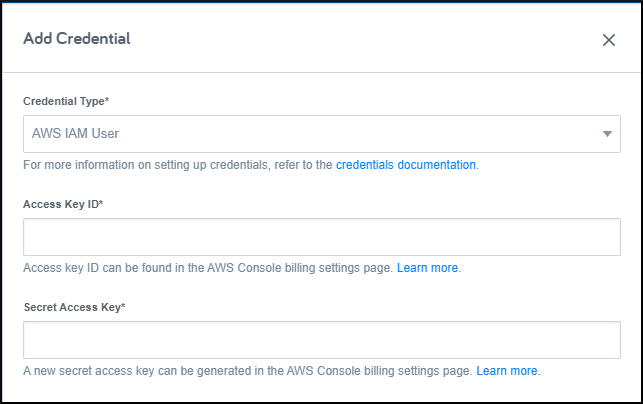
Follow the AWS instructions for creating a user.
- For
Access type, selectProgrammatic access. - Specify which AWS permission policies are attached to the role based on the Flexera policies that you will be using.
Once the user has been created copy the Access key ID and press the Show link to expose and copy the Secret access key. Copy these two values into the corresponding fields in Flexera.
API Usage
Details for creating an AWS IAM user credential using the API can be found in the API docs using the scheme aws.
The standard provider name to match credentials in Flexera-built policies for AWS is: aws
Key rotation
To rotate the credential, select the credential, press the Edit button, and provide the new Access key ID and Secret Access Key from AWS. Any policy using the credential will use the new keys the next time it is evaluated.
Azure
Microsoft Azure provides multiple APIs with different authentication types for different capabilities. Depending on the policy you may need to set up one or multiple different credential types. Each policy specifies which kind of credential is required.
Azure Resource Manager
The Azure Resource Manager (ARM) APIs provide the ability to gather data and interact with resources in subscriptions via App Registrations.
In Flexera Governance, navigate to the Credentials page, press the New Credential button, and select the Microsoft Azure Resource Manager credential type.
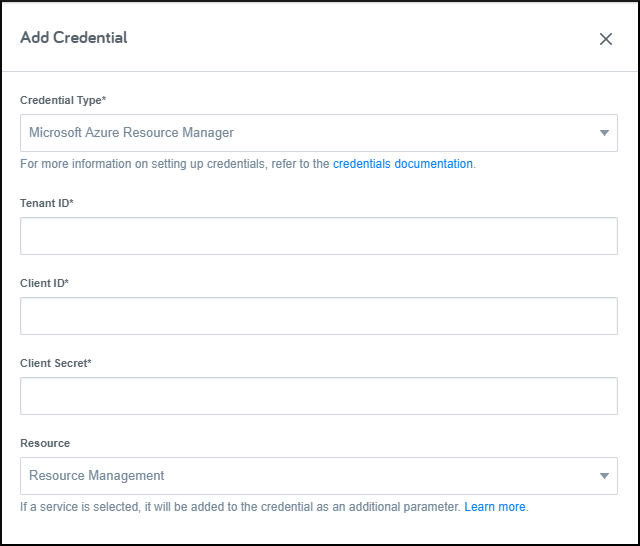
To learn more about Azure app registrations and how to create them, see the Azure documentation.
When creating your app registration, select the account type of: Accounts in this organizational directory only (<YOUR DIRECTORY NAME HERE> only - Single tenant). Once you've created the app registration, get a client secret for it in the Certificates & Secrets page by creating a New client secret. Take care if selecting an expiration date for the client secret to set a reminder to rotate the credential in Flexera before it expires.
After creating the app registration, follow the Microsoft instructions for granting the app access to your subscriptions. Take note that Flexera-built policies using the credential will run against all subscriptions the app has access to.
Get the following information from Azure and place it in the corresponding field in Flexera.
| Credential field | Value |
|---|---|
Tenant Id |
Directory (tenant) ID value from Azure |
Client ID |
Application (client) ID value from Azure |
Client Secret |
The Client secret Value from Azure (take note of the expiration date so you can rotate the credential before it expires) |
For the Resource field, select the type of service that this credential will be used to interact with. If the app registration can interact with all services, a seperate Credential resource will need to be created for each one.
| Field Value | Description |
|---|---|
Resource Management |
Used for policies that interact with the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) APIs |
Azure Active Directory |
Used for policies that interact with the Microsoft Active Directory (AD) (sometimes called Graph) API |
Log Analytics |
Used for policies that interact with Azure Log Analytics to gather detailed metrics on resource usage |
API Usage
To create Azure RM credentials using the API, use the oauth2 credential scheme with the following values:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
grant_type |
client_credentials |
token_url |
Directory (tenant) ID value from Azure formatted as (without the quotes): https://login.windows.net/{TENANT_ID}/oauth2/token. (e.g. https://login.windows.net/123456789-1234-1234-1234-123456789012/oauth2/token). Note this value can also be found by clicking on the Endpoints button and copying the endpoint titled OAuth 2.0 token endpoint (v1)) |
Submit the request with the client_credentials_params hash populated with the following values:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
client_id |
Application (client) ID value from Azure |
client_secret |
The Client secret Value from Azure (take note of the expiration date so you can rotate the credential before it expires) |
additional_params |
Set the resource field to the value corresponding to the service this credential will be used for. Valid values are listed below. |
| Resource field value | Description |
|---|---|
https://management.azure.com |
Used for policies that interact with the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) APIs |
https://graph.microsoft.com |
Used for policies that interact with the Microsoft Active Directory (AD) (sometimes called Graph) API |
https://api.loganalytics.io |
Used for policies that interact with Azure Log Analytics to gather detailed metrics on resource usage |
https://my_azure_storage_account.blob.core.windows.net |
Used for policies that interact directly with storage accounts. Replace my_azure_storage_account with the name of the storage account. One credential must be created for every storage account. |
The standard provider name to match credentials in Flexera-built policies for AWS is: azure_rm
Key rotation
To rotate the credential, select the credential, press the Edit button, and provide the new client secret Value from Azure. Any policy using the credential will use the new keys the next time it is evaluated.
Azure Enterprise Agreement
The Azure Enterprise Agreement (EA) Reporting APIs provide the ability to gather information primarily related to billing and consumption data.
In Flexera Governance, navigate to the Credentials page, press the New Credential button, and select the Microsoft Azure Enterprise Agreement credential type.
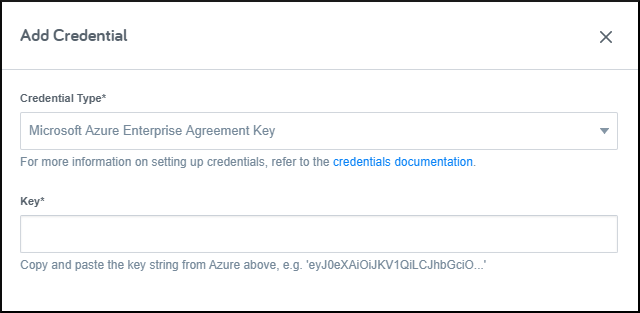
Follow the Microsoft instructions on how to Generate or retrieve the API key
. Take note of the key's expiration date and set a reminder to rotate the credential in Flexera before it expires.
Enter the key value in the Key field in Flexera.
API Usage
To create Azure EA credentials using the API, use the api_key credential scheme with the following values:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
location |
header |
field |
Authorization |
type |
Bearer |
key.data |
Enter the API key retrieved from Microsoft |
key.type |
plain |
The standard provider name to match credentials in Flexera-built policies for Azure Enterprise Agreement is: azure_ea
Key rotation
To rotate the credential, select the credential, press the Edit button, and provide the new API key value. Any policy using the credential will use the new keys the next time it is evaluated.
In Google cloud, service accounts are the preferred method for API authentication.
In Flexera Governance, navigate to the Credentials page, press the New Credential button, and select the Google Compute Engine Service Account credential type.
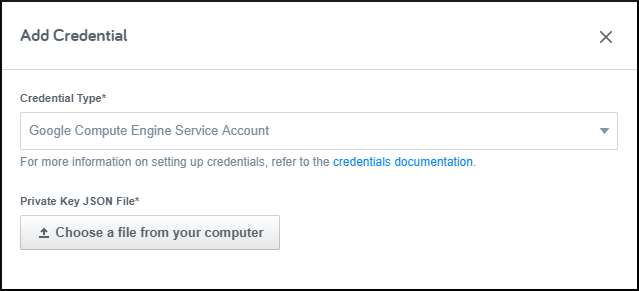
Follow the Google documentation to create a service account.
Grant the service account access to whichever GCE projects you want, taking note that Flexera-built policies using the credential will run against all projects the app has access to.
When creating the key, choose the JSON key type, which will download a JSON file onto your machine.
In Flexera, press the button to select the file that you just downloaded.
API Usage
To create Google credentials using the API, use the oauth2 credential scheme with the following values:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
grant_type |
jwt_bearer |
token_url |
https://accounts.google.com/oauth2/v4/token |
Submit the request with the jwt_bearer_params hash populated with the following values:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
additional_claims.scope |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform |
alg |
RS256 |
aud |
"" |
max_minutes |
60 |
iss.data |
The value of client_email from the JSON file (without the quotes) |
iss.type |
plain |
signing_key.data |
The value of private_key from the JSON file (without the quotes) |
signing_key.type |
plain |
The standard provider name to match credentials in Flexera-built policies for AWS is: gce
Key rotation
To rotate the credential, select the credential, press the Edit button, and provide the new JSON file. Any policy using the credential will use the new keys the next time it is evaluated.
Oracle
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure recommends using Oracle API Signing Keys for authenticating with Oracle Cloud APIs.
Follow the Oracle Cloud API Signing Key guide to create an Oracle API Signing key.
Note: This credential type is not yet supported in the RightScale Dashboard or the Flexera One User Interface.
API Usage
To create oracle credentials using API, use the oracle credential scheme with the following values:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
fingerprint.type |
plain |
fingerprint.data |
Value of fingerprint returned after creating API key in Oracle Cloud |
password.type |
plain |
password.data |
Password used to encrypt the private key (This is an optional field. Provide the password only if you have used a password to encrypt your private key) |
privateKey.type |
plain |
privateKey.data |
Private Key (in PEM format) equivalent of the public key used to create Oracle Cloud API key |
tenancyOcid.data |
plain |
tenancyOcid.type |
Oracle Cloud Identifier of your tenancy |
userOcid.type |
plain |
userOcid.data |
Oracle Cloud Identifier of the user calling the API |
Key rotation
To rotate the credential, use Update Oracle Credential API. Any policy using the credential will use the new keys the next time it is evaluated.