Overview
RightScale Policy Management allows you to automate governance across your multi-cloud environment to increase agility and efficiency while managing security and risk in your organization. The capability is purpose built to leverage an intelligent policy engine that lets you enforce rules and best practices to help you achieve your business outcomes like saving time, cost reduction, increasing utilization, and rightsizing your cloud environment.
Key Capabilities
- Built-in Policies for Cost, Security, Operational, and Compliance use cases
- Dry run policies and then configure them to take approved actions on any API backed cloud, service, and resource
- Automate policies across your entire cloud landscape (multiple accounts)
- Maintain policy-as-code using the built-in policy template language to write your own policies
- Policies can enforce rules on any cloud or any service with an API
- Automate your policies using the fully-featured Policies API and documentation
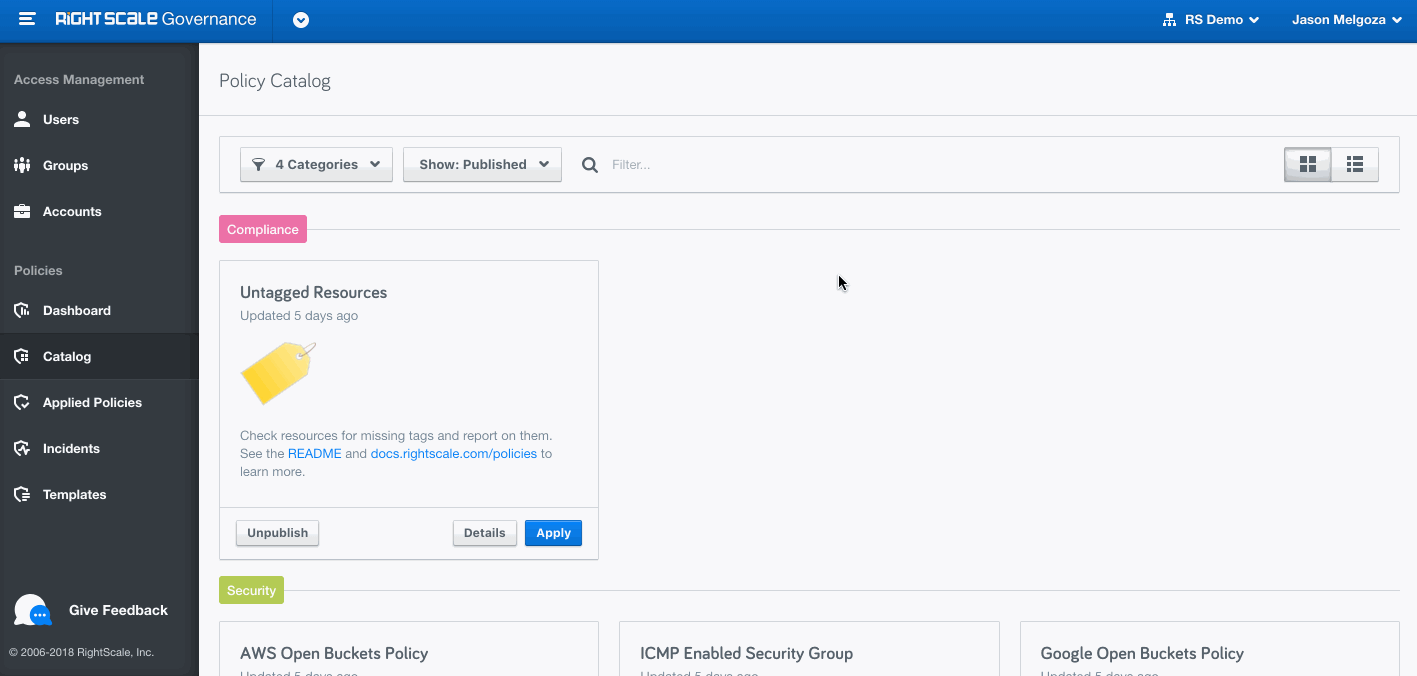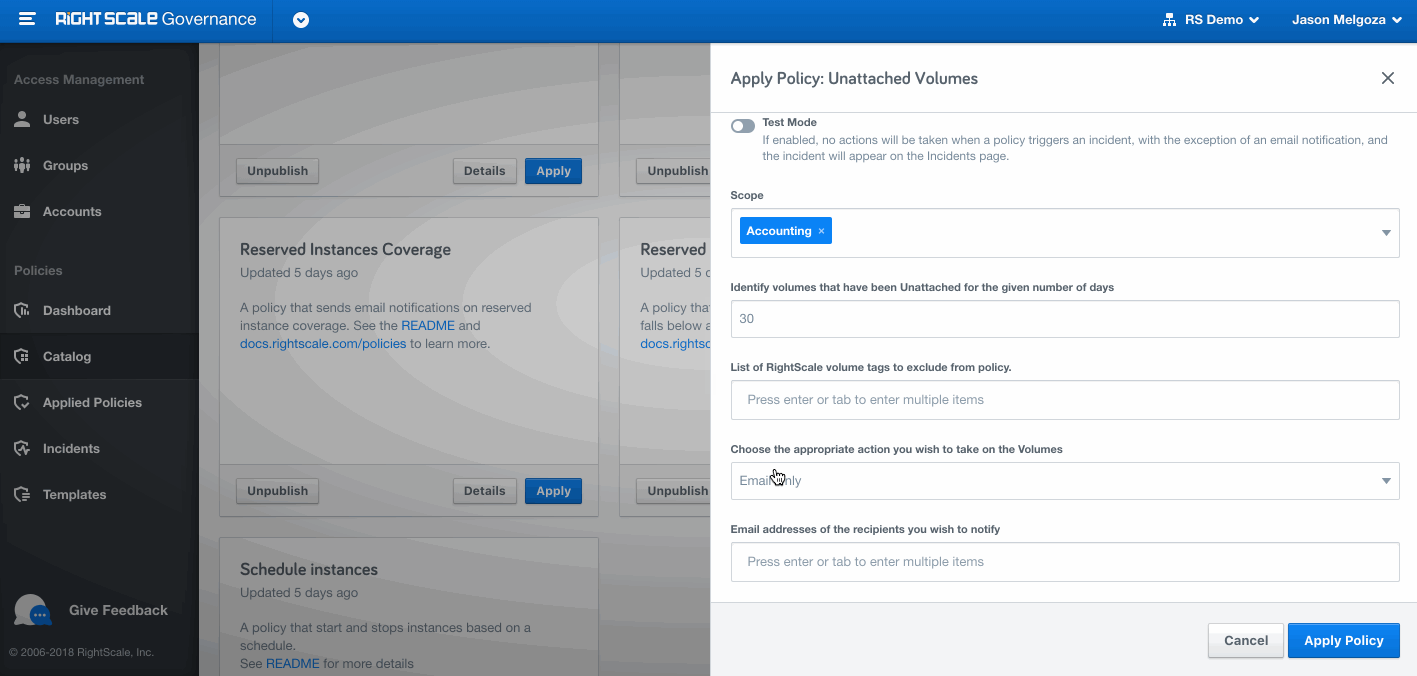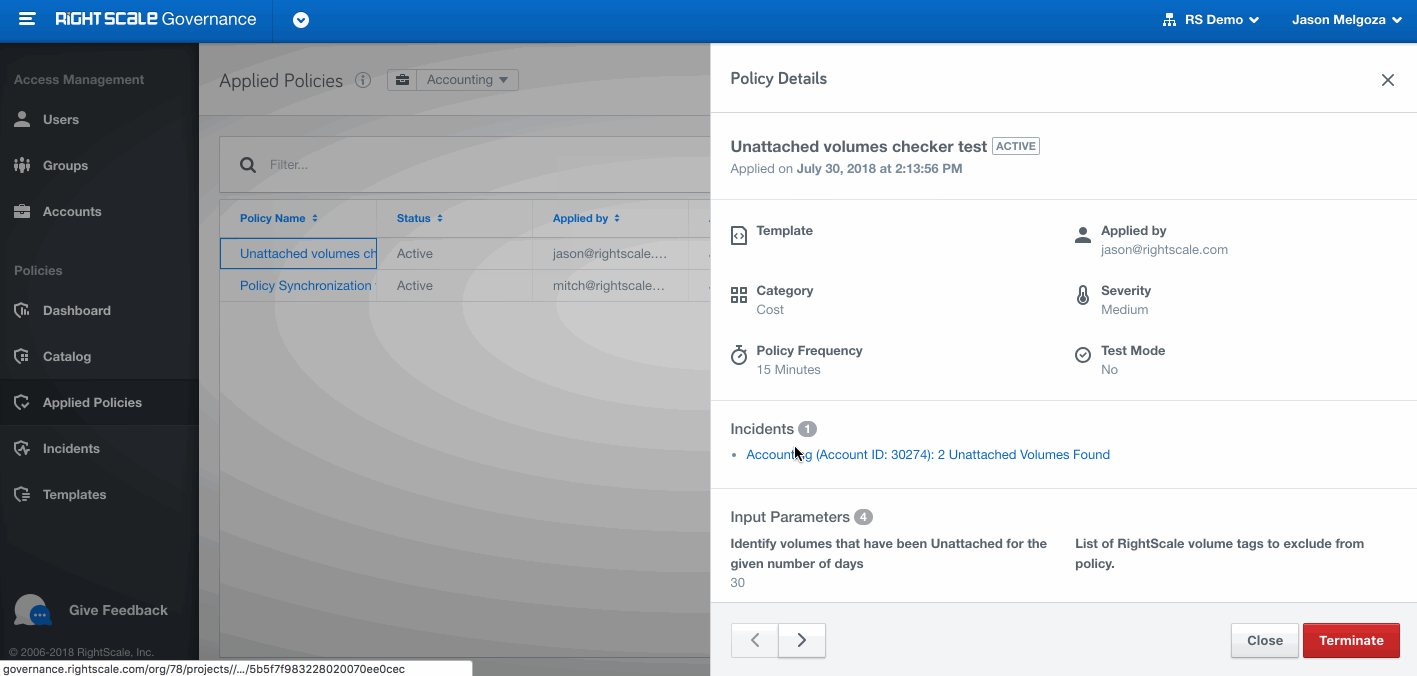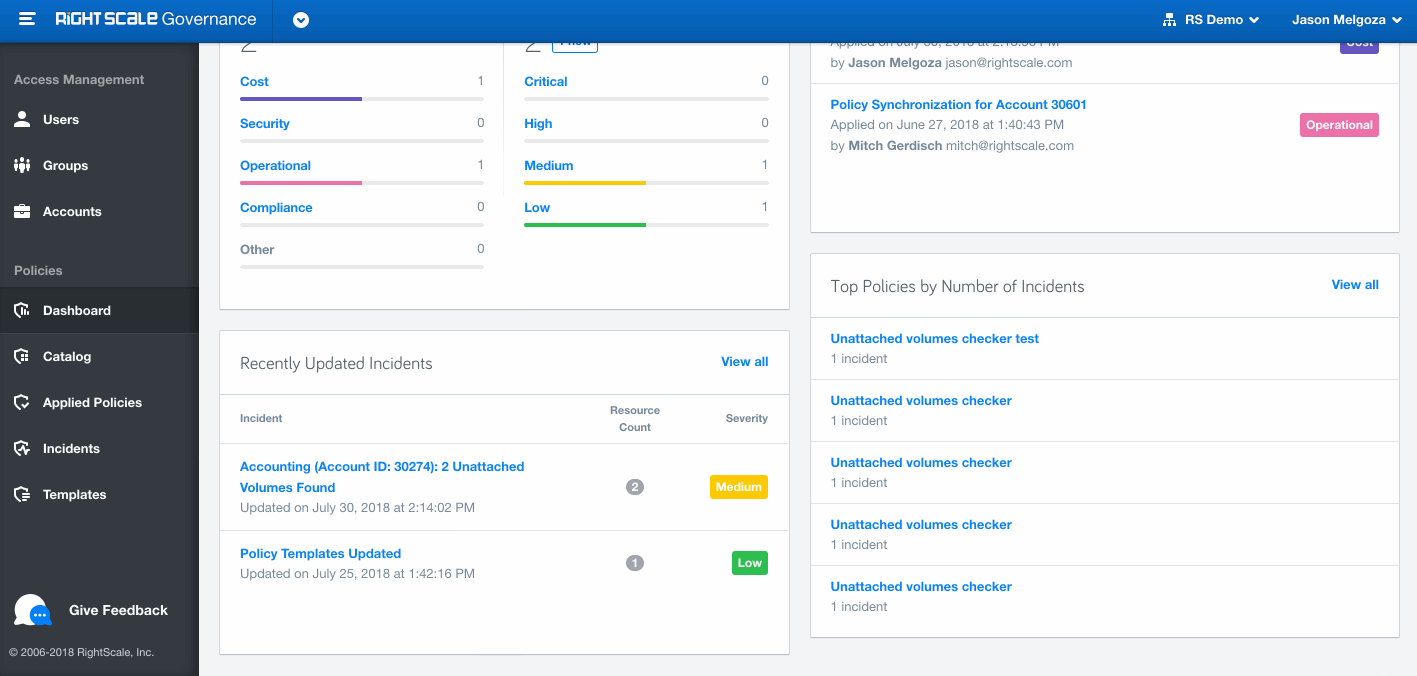
Policy Use Cases
RightScale developed a wide variety of built-in policies that provide high value with minimal effort on Day 1. You can simply select the policy you are interested in, customize it, and apply it to individual accounts or across multiple accounts to achieve your business outcomes. Find the complete list here.
In addition to following examples, the policy engine supports writing custom policies to help customers achieve custom requirements and not be limited by what RightScale provides out of the box.
Cost
Increase cost visibility and management in your multi-cloud world and take appropriate actions to run an efficient infrastructure.
- Identify where you are wasting spend and realize immediate savings
- Collaborate to reduce future cloud costs
- Use tagging as a foundation for ongoing cost management
- Automate waste prevention
Security
Gain visibility and control across all your public and/or private cloud environments with our security policies. Improve security across your applications, data, and associated infrastructure by finding security vulnerabilities before your customers do.
- Secure public storage buckets
- Take control of your security groups
- Monitor and secure IAM access
Operational
Save valuable human time and investment by automating everyday IT operations. Running an automated and efficient cloud infrastructure frees up expensive resources on high ROI projects like scaling, growth, and deliver value faster than anyone else.
- Reduce waste by putting instances on schedule
- Put automatic key rotation to avoid downtime
Compliance
Enterprises typically have multiple compliance requirements but struggle to automate them which leads to downtime as well as resource waste. By having a strong compliance strategy but also ability to quickly automate it provides peace of mind and avoids business interruption.
- Ensure comprehensive tagging strategy
- Write custom policies for HIPAA, GDPR, PCI, and more
Policy Actions
Policy Engine leverages our multi-cloud orchestration platform written in Cloud Workflow Language that allows managing entire applications running on the cloud. Actions can be defined that help remediate policy incidents or that trigger other automation to report on incidents.
The sequence of actions that occur when an incident is detected is defined in the policy template. At any point in the sequence, manual approval steps can be inserted that require an authorized user to press an Approve
button in the UI (or equivalent API call) before the sequence is resumed. Actions can also be run manually. When applying a policy, the policy manager can choose to skip all defined approval steps so that the action sequence runs fully automated immediately when an incident is detected. In this case the incident details will show that the approval steps were skipped.
Examples
- Start/Stop instances
- Change (downsize) instances
- Add/Remove Tags
- Add/Terminate/Delete resources (e.g.: Unattached volumes, old snapshots)
- Migrate between storage classes
- Slack and Email Notifications
- Running Operational Runlists
- Scaling Server Arrays
- Retrieving and analyzing metrics data
- Sending requests to external applications
Basic Concepts

Policy Template
Open source Policy definition, written in powerful Policy Template Language, that defines the blueprint of a Policy. It specifies input parameters, conditions, and actions the policy will take when it is triggered. You can use built-in policy templates from RightScale as is or customize the source code to create your own custom policy. Policy Template can be published to the Catalog to make it visible to the entire organization.
Applied Policy
A running policy that has been applied from a policy template. It inherits all the properties of the policy template. One policy template can be applied as many times as needed with different input parameters. For example, you could apply a policy that looks for unattached volumes to development accounts and production accounts with different parameters and resolution actions. In development accounts, you could configure the applied policy to automatically delete unattached volumes after 3 days, while in the production accounts, you could simply send an email alert.
Credentials
In order to gather information and, in some cases, take action, policies need to be able to reach out to other APIs. While some policies interact only with other Flexera APIs, many policies interact directly with service provider APIs. In these cases, the system must have credentials for those APIs. The Credentials page provides a central location to enter, manage, and update credentials that can be used by policies. Credentials can only be managed by users with enterprise_manager role on the Organization or admin role on the Project, but all users that can apply policies have access to use credentials while applying a policy.
Incident
When the conditions of the applied policy are met, an incident is created. It contains all the information about why the policy was triggered and the current status. One applied policy can have more than 1 incident. Incidents can be in one of the following states:
active- one or more conditions were found to be true during the policy check (this state is calledtriggeredin the API)resolved- the conditions that created this incident no longer exist, or theresolve_incidentfunction was calledterminated- the applied policy was terminated while the incident was active
Incidents that are not actionable (they are terminated or resolved with no pending actions) are archived after 30 days and available only via the API.