Policy Actions
Policy Engine leverages our multi-cloud orchestration platform written in Cloud Workflow Language that allows managing entire applications running on the cloud. These actions may include adding an approval prior to executing a set of automated actions. As well as choosing which items in 'violation' to perform the action on.
Examples
- Start/Stop instances
- Change (downsize) instances
- Add/Remove Tags
- Add/Terminate/Delete resources (e.g.: Unattached volumes, old snapshots)
- Migrate between storage classes
- Slack and Email Notifications
- Running Operational Runlists
- Scaling Server Arrays
- Retrieving and analyzing metrics data
- Sending requests to external applications
Basic Concepts

Policy Template
Open source Policy definition, written in powerful Policy Template Language, that defines the blueprint of a Policy. It specifies input parameters, conditions, and actions the policy will take when it is triggered. You can use built-in policy templates from RightScale as is or customize the source code to create your own custom policy. Policy Template can be published to the Catalog to make it visible to the entire organization.
Applied Policy
A running policy that has been applied from a policy template. It inherits all the properties of the policy template. One policy template can be applied as many times as needed with different input parameters. For example, you could apply a policy that looks for unattached volumes to development accounts and production accounts with different parameters and resolution actions. In development accounts, you could configure the applied policy to automatically delete unattached volumes after 3 days, while in the production accounts, you could simply send an email alert.
Incident
When the conditions of the applied policy are met, an incident is created. It contains all the information about why the policy was triggered and the current status. One applied policy can have more than 1 incident. Incidents can be in one of the following states:
active- one or more conditions were found to be true during the policy check (this state is calledtriggeredin the API)resolved- the conditions that created this incident no longer exist, or theresolve_incidentfunction was calledterminated- the applied policy was terminated while the incident was active
Incidents that are not actionable (they are terminated or resolved with no pending actions) are archived after 30 days. They are accessible via the UI or via the API. Archived incidents are currently available indefinitely, but may be deleted after a set time period in the future.
Key Policy Constructs
There are several key concepts in Policies that will help you better understand both RightScale policies as well as writing your own custom policies.
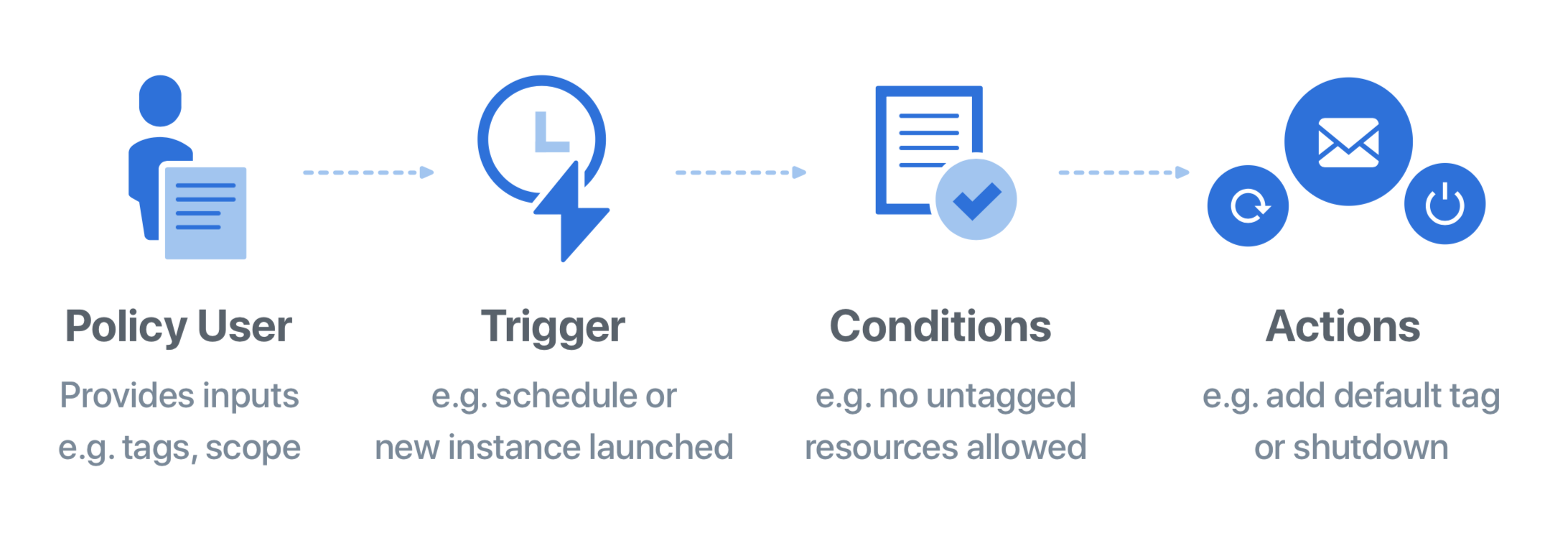
Trigger
An event, action or schedule that activates a policy execution to check for the condition (e.g. Every 15 minutes).
Conditions
Rules that are evaluated when a policy is activated (e.g. ensure instances always have required tags).
Action
Remediation that a policy takes when the conditions are met. These actions could be fully automated or can be set to get an approval prior to executing the automated actions, e.g. approve deleting all the unattached volumes detected by the policy and send email notification. An action is either an escalation or a resolution.
Escalation
Defines the actions which are triggered when there is one or more violation found during validation. Actions can either be fully automated, automated with approval or can be run manually on all resources or a selected set of resources. An example of a escalation is sending an email reporting on the violation data. Escalations can only be run before the violation is resolved.
Resolution
Defines the actions to be taken when a policy violation is resolved. Defined as resolution in the policy template. These actions could be fully automated or can be set to get an approval prior to executing the automated actions, e.g. approve closing a JIRA ticket as part of the resolution.
Writing your own Policy
We built the policy engine with a very important goal of keeping it open source so users can either customize RightScale built-in policies or write their own based on the custom requirements.
Get started with writing your custom policies using the Policy Template Language.
API Documentation
Policy management has extensive APIs that are publicly available to the customers.