Sign-Up for Amazon S3
Visit the following link for information on signing up for AWS S3...
Create a New S3 Bucket
Overview
In S3, a bucket is essentially a folder where you can store files in the Amazon cloud. Think of S3 as one big hard drive that everyone shares. As a result, you'll have to create unique bucket names. You will not be able to create generic bucket names like files
or images.
Therefore, it's a good idea to add your application name as a prefix to any bucket name (e.g. myapp-images). The maximum number of S3 buckets per account is 100. The ownership of an S3 bucket is associated with your AWS Account Number and is non-transferrable. However, if a bucket is deleted, its name can be used to create a new S3 bucket in any AWS account.
As a best practice, create S3 buckets where the name is all in lower-case letters. Refrain from using underscores (_) as it's been known to cause problems at the DNS level. If you are using one of RightScale's MySQL ServerTemplates that support continuous backups of your database to S3, you need to specify an S3 bucket where the mysqldump files will be stored and retrieved. You should create an S3 bucket for this purpose before you launch a MySQL server.
Upper-case and lower-case letters are considered unique characters. For example, you can create an S3 bucket with the name 'MyBucket' and another bucket with 'mybucket' as its name.
Watch out for two servers that backup into the same S3 bucket with the same prefix. You'll run into problems if you Clone
a Deployment and forget to rename the prefix or the name of the S3 bucket before launching the Server.
Use the procedure outlined below to create a Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket for data storage and retrieval.
Prerequisites
- 'actor' user role privileges in the RightScale account.
- If you plan to use the MySQL Backup feature in the RightScale ServerTemplates, be sure to make an S3 bucket first before you use the ServerTemplates.
Steps
At a minimum, you need to create an S3 bucket that you can later use to upload a dump (*.gz) of your MySQL database. If you are not using an SVN repository, you may want to create a separate bucket where you can store a tarball of your application code, which will be used by your Application Servers to retrieve your web application.
Create an S3 Bucket
To create an S3 bucket which you will use to store a mysql dump of your database...
- Go to Clouds > AWS Global > S3 Browser. Click New Bucket.
[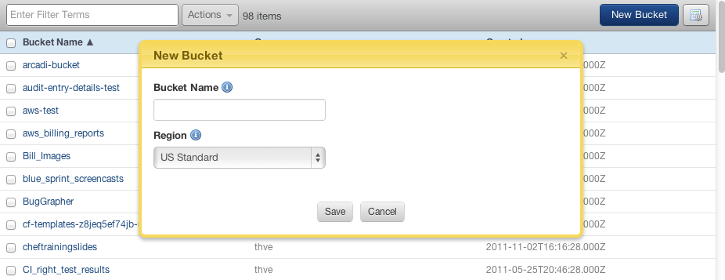
- Bucket Name - Remember, the S3 namespace is global, so it might be hard to find a generic bucket name that's not already being used by someone else. Therefore, you might want to use your company or project name as a prefix for your bucket name. For example, 'myproject-db' or 'myproject-app'. It is recommended that you use only lower case letters when naming your S3 bucket. This is because of a backwards compatibility issue: S3 is case sensitive, but DNS is not, so there is ambiguity when mapping bucket names to hostnames. Also, you are not allowed to use spaces or periods in the bucket name. See What are Valid S3 Bucket Names?
In order to access the bucket from the web, the name must be a valid DNS hostname.
- Region - Although the namespace of an S3 bucket is global, the actual location of the bucket exists in a particular AWS Region. Therefore, for performance reasons, you should create the S3 bucket in the AWS Region that's in the same geographic region as a majority of your customers/visitors. Similarly, you will also want to launch your servers in the same geographic region. Select the desired region from the dropdown.
US Standard (i.e. US-East) is the default region for a new Amazon S3 bucket.
- Click Save.
If you are going to pull your application code from an S3 bucket instead of from an SVN repository, create a second bucket for your application code (e.g. myproject-app).
Keep in mind that you will not be able to delete a bucket until all of its contents have been deleted. In addition, although EBS Snapshots are technically stored in S3 as well, they are not accessible via the S3 Browser.
Upload Files to an Amazon S3 Bucket
Overview
After you Create an S3 Bucket, you will need to upload files and apply permissions to an S3 Bucket. Use the procedure outlined below to upload files to a Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket and apply appropriate permissions.
Prerequisites
- 'actor' user role privileges in the RightScale account.
- If you plan to use the MySQL Backup feature in the RightScale ServerTemplates, be sure to make an S3 bucket first before you use the ServerTemplates.
Steps
Upload Files
- Navigate to Clouds > AWS Global > S3 Browser
- Create a New Bucket or click on the bucket name text link.
- Once in the bucket, you have a choice to add New Folders or Upload File(s).
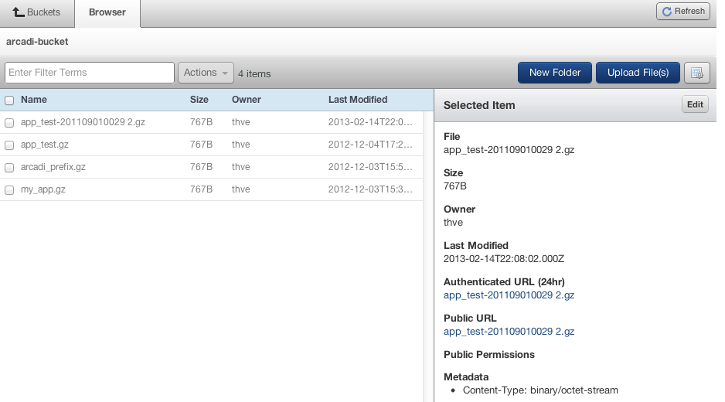
- You can select Add Files... to browse for files or drag and drop files from your system into your S3 bucket. By default, each file that is uploaded will have its permissions set as private.
A 'private' file will only be accessible to resources of the same AWS Account. In order to retrieve a 'private' file, you will need to pass your AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secret Access Key. (In future tutorials, where a script is run on a Server to retrieve an object in an S3 bucket, Credentials that RightScale has automatically created for your account (AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY) will be used for retrieval validation purposes.)
If you're dealing with a dump of your database, you will probably want to keep it private, but you may want to make other objects available to the public.
Make an S3 Object Public
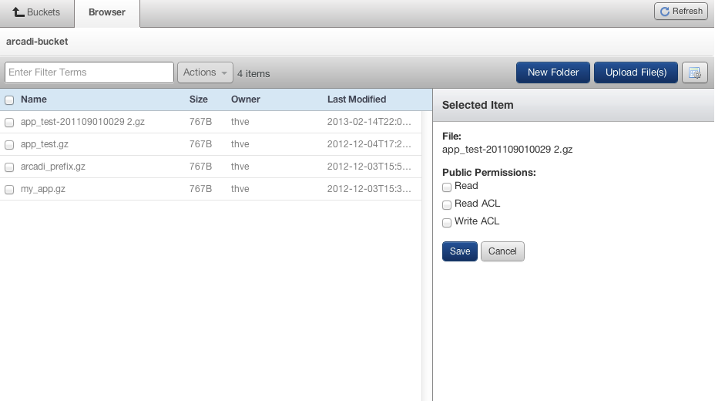
- If you want an object to be publicly accessible, click on the item and select Edit in the window that will appear on the right.
and 'Set Object Permissions.'
An S3 Object Permissions can be set to the following:
- Read - Any public user can read an object and its metadata.
- Read ACL - Anyone with access to the account can read the object and its metadata.
- Write ACL - Allow anyone with access to the account can create, overwrite, and delete an object.
Click Save.
[
Reminders
- You will not be able to delete a bucket until all of its contents have been deleted.
- Although EBS Snapshots are technically stored in S3 as well, they are not accessible via the S3 Browser.
Run S3 Analysis
Overview
After you create an S3 Bucket and upload files, you can run analysis on the bucket. Use the procedure outlined below to run analysis on a Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket.
Prerequisites
- 'actor' user role privileges in the RightScale account.
- an S3 bucket with previous activity.
Run Analysis
- Navigate to Clouds > AWS Global > S3 Browser and select a bucket.
- Once in the bucket, click on the Analysis tab.
- Click Run analysis.
View Analysis
Each time you click the Run analysis button, you are generating a report. Your reports are saved and stored in the Analysis tab by month and year. Click on a month to uncollapse all the reports available from that timeframe.
Your report displays the following information for the entire bucket:
- Total objects: this is the number of objects stored in the bucket, e.g., images, snapshots etc.
- Total size: this is the total size of the collective objects stored in your bucket.
- Started at: this is the timestamp for when the analysis was run.
- Completed at: this is the timestamp for when the analysis completed.
For each section you may:
- Change the sorting of the columns by clicking the column title.
- Enter filter terms in the filter box. Filtering by any characters displayed in the list will return results, e.g.,
2007
or25
orMiB
. - Download this section of the report as a CSV by clicking
Download as CSV
hyperlink at the bottom left corner of the window. - Collapse sections you would like to hide.
Usage by Month
With the Usage by Month
section you have the option of viewing usage by Month, Number of Files, and Total Size. Use the settings icon in the upper right corner of your 'Usage by Month' window to determine which columns you want to view. You may view the Number of Files and Total Size of the bucket for each Month of the bucket's existence.
Usage by Size
With the Usage by Size
section you have the option of viewing usage by Size and Number of Files. The Size column in this section specifies the ranges of MiB and the Number of Files that exist for each range.
Usage by Prefix
With the Usage by Prefix
section you have the option of viewing usage by Prefix and Size. The Prefix column specifies the folder names within your bucket. The Size specifies the total size of the contents of the folder.
Delete an S3 Bucket
Overview
You can only delete an S3 bucket if it's empty and doesn't contain any files. Once an S3 bucket has been deleted, another user with an AWS account will be able to create an S3 bucket with the same name. Therefore, you should only permanently delete an S3 bucket if you do not want to use an S3 bucket with that name. use the procedure outlined below to delete an existing Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket.
Prerequisites
- 'actor' user role privileges in the RightScale account.
Steps
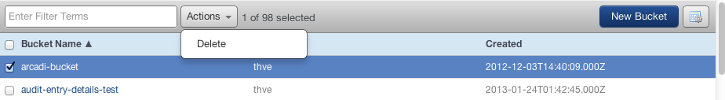
- Go to Clouds > AWS Global > S3 Browser.
- If there are any files in the bucket, you will need to manually delete all of the files before you can delete the bucket. Once all items in the bucket are removed, you can select the S3 bucket, click Actions, and 'Delete' the bucket.