Overview
RightScale provides support for Azure Resource Manager (also called ARM or AzureRM) APIs. This is the 2nd generation “cloud” offering from MS Azure, and is significantly different from their earlier implementation.
Resource Mappings
As RightScale abstracts many different cloud resources in our API and UI, we must map resource offerings
from clouds into RightScale resources. The table below lists the resource mappings as they relate to ARM.
Note that unless indicated otherwise, all resources and functionality described below will be supported
in the Dashboard, CM API 1.5, and Self-Service CAT files.
| Azure Resource | RightScale Resource | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Platform Image | Image | With property visibility = public |
| Marketplace Image | Image | 1. With property visibility = public 2. Marketplace images must be “enabled” in Azure before using in RightScale. 3. Images are refreshed once every 24 hours from Azure |
| User Image | Image | 1. With property visibility = private 2. Unmanmaged images must be stored within the system container of a storage account. Example:<StorageAccount>/system/Microsoft.Compute/Images/vhds/Win2012R2wRL10-osdisk.08877202-d144-4c8e-bd97-695c3b848b88.vhd 3. Vhd blob metadata must be set as follows: MicrosoftAzureCompute_ImageType = OSDisk MicrosoftAzureCompute_OSType = Linux or Windows |
| VMs | Instances | |
| VM Size | Instance Type | |
| Virtual Machine | Instance / Server | |
| Public IP Address | IP Address | 1. Only those with ‘static’ allocation are listed. Those with ‘dynamic’ allocation are not listed but can be used when launching by setting the ‘associate_public_ip_address’ flag 2. Public IP Addresses created in RightScale will be associated with the “default” Resource Group for the region |
| Network Interface | Network Interface | |
| Network Security Group | Security Group | Security Groups created in RightScale will be associated with the “default” Resource Group for the region. Limitations |
| Network Security Group - Security Rules | Security Group Rule | Limitations |
| Virtual Network | Network | |
| Resource Group | Deployment | |
| Storage Account | Placement Group | Microsoft - About Disks and VHDs |
| Virtual Network - Subnet | Subnet | |
| Network Interfaces | IP Address Bindings | |
| Disks | Volumes | ARM Managed Disks and Storage Account based VHDs are discovered as Volumes in RightScale. Microsoft - Overview of Managed Disks Microsoft - About Disks and VHDs |
Resource Descriptions
Azure Resource Groups
RightScale will create and manage Resource Groups in Azure in 3 specific cases:
- Default Resource Groups
- Deployment-related Resource Groups
- Instance-related Resource Groups
In addition to creating Resource Groups in the above scenarios, RightScale will also attempt to cleanup
Resource Groups created by RightScale in certain scenarios. Details for this behavior are below.
Default Resource Groups
RightScale will create a default Resource Group for each ARM region when needed. This default Resource Group will be named: rs-default-[region] (e.g. rs-default-eastus). The default Resource Group will contain the following types of resources if a deployment is not specified when creating them: Networks, Subnets, Security Groups, IP Addresses, and Placement Groups (Storage Accounts).
Some of the above resource types are created automatically by the RightScale platform when launching a VM. In these cases, the resources are placed in the Deployment-related Resource Group.
These default Resource Groups will not be auto-removed per the procedure listed below, however they can be deleted via the Azure Portal. If a default Resource Group is deleted in Azure, it will be recreated when a resource type that belongs in the default Resource Group is created from RightScale.
Deployment-related Resource Groups
In Azure Resource Manager, Resource Groups are a construct meant to group together resources that have a similar lifecycle. The clear parallel in RightScale is the Deployment. For this reason, you can associate a Deployment in RightScale with a Resource Group in ARM. Once this association is established, tags will be synchronized between the two. Any instance/server/array launched in the Deployment will launch into the associated Resource Group. Likewise, any resource created natively in ARM in that Resource Group(after the association has been created) will show up in the associated RightScale Deployment.
RightScale creates a Resource Group in ARM when the first ARM server, Network, Subnet, Security Group, IP Address and placement group in the Deployment is launched/created, and this Resource Group is used for all servers/arrays/instances in that Deployment thereafter. The Resource Group in ARM will be named after the Deployment name in RightScale (sanitized to meet Azure naming rules).
If a resource is moved to another Deployment in RightScale, its Resource Group is not modified. This means that there is the possibility that a resource in a given RightScale Deployment may not be in the associated Resource Group.
Resource Groups that are created by RightScale to manage Deployments will have two Azure Billing Tags named RightScale Deployment and RightScale Deployment Href. These tags impact the management of Resource Groups by RightScale and should not be removed.
Instance-related Resource Groups
If an Instance (not Server) is launched through RightScale without an associated Deployment RightScale, a Resource Group is created specifically for that instance. The Resource Group in ARM will be named after the Instance name in RightScale (sanitized to meet Azure naming rules).
If the instance is moved to a Deployment in RightScale, its Resource Group is not modified.
Resource Groups that are created by RightScale to manage an Instance will have two Azure Billing Tags named RightScale Deployment and RightScale Deployment Href. These tag impact the management of Resource Groups by RightScale and should not be removed.
Resource Groups and Resources
For any resource in RightScale that exists in a Deployment, including instances, servers, IP Addresses, PlacementGroups, SecurityGroups, and Networks, its Resource Group is automatically set by RightScale when it is launched, using the Resource Group associated with the Deployment (or a new Resource Group if one is not associated).
Note that some of these resources are not visible in the RightScale Deployment
view, but they are associated with a deployment when being created and will have a Deployment
link in the API. For any resource that is created without an associated Deployment, it is created in the Default Resource Group for the region.
Associating a Resource Group and a Deployment
If you would like a Deployment to be associated with a specific Resource Group, you can edit the Deployment and pick from any existing available Resource Group in ARM. If you pick 'None', then one will be created when needed (when a resource in the Deployment is created/launched).
When you associate an existing Resource Group with a Deployment, any new resources discovered in Azure from that point forward will automatically be placed in the associated Deployment and any existing resources will remain outside of that deployment.
You can change the associated Resource Group at any time. When you do so, the tags will start syncing to the new Resource Group, but any running resources in the Deployment in RightScale will not be modified - they will continue to exist in the Resource Group in which they were created.
As mentioned above, if a resource is created/launched in a Deployment that does not have a Resource Group associated with it, RightScale creates a new Resource Group in ARM with a similar name to the Deployment (sanitized per Azure naming conventions). In particular, this happens when a server/array/instance is launched or a Placement Group/Network/Security Group/IP Address is created and the Deployment does not have an associated Resource Group.
Cleanup of Resource Groups
For any Resource Group that is created by RightScale, the Resource Group will be deleted from Azure once the Deployment is deleted from RightScale.
Deleting Deployments
A Deployment in RightScale can be deleted once all of the associated cloud resources have been removed. For instances/servers/arrays, this means that there are no running instances in the cloud. For other resources, such as Networks/IP Addresses/Placement Groups/Security Groups, the resource must actually be deleted or disassociated from the Deployment before the Deployment can be deleted.
Deleting a Deployment in RightScale that is associated to a Resource Group in ARM will also delete the Resource Group in ARM, if that Resource Group was created by RightScale.
Managed Disks
Azure Managed Disks remove the requirement of managing Storage Accounts to contain your VM disks. You no longer have to create Storage Accounts and ensure you are are not exceeding their service limits. [Microsoft - Azure Managed Disks Overview]
RightScale discovers Azure Managed Disks as Volumes in RightScale -- the Resource UID will be the GUID of the disk, and it will list the Volume Type instead of the Placement Group.
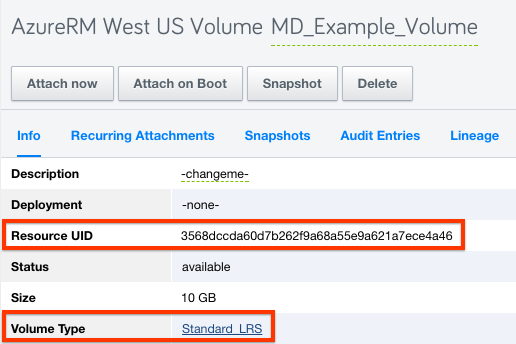
When creating a new Server, Instance or ServerArray in the Cloud Management UI, it will use Managed Disks by default. You are still able to use unmanaged disks if you prefer -- in this case you will be required to specify an existing or new Placement Group (Storage Account).
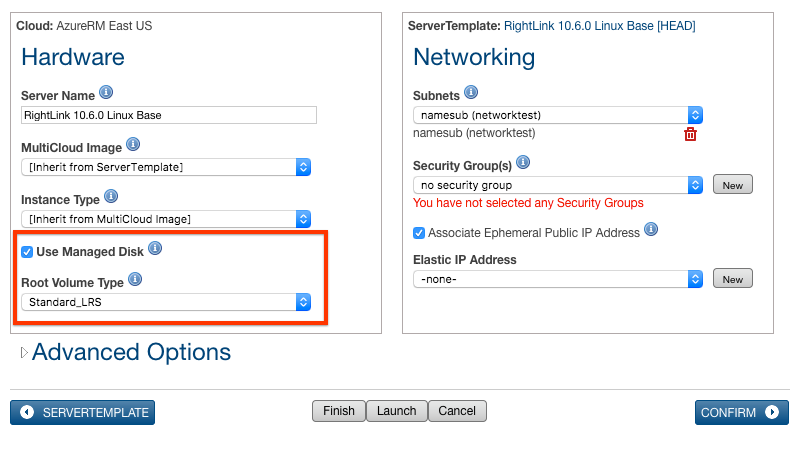
When creating a new Server, Instance or ServerArray via the API or Self-Service, the root_volume_type_uid attribute within the cloud_specific_attributes hash needs to be set to Standard_LRS or Premium_LRS based on the type of Managed Disk you want to provision.
cloud_specific_attributes do {
"root_volume_type_uid" => "Standard_LRS" # Possible values: Standard_LRS, Premium_LRS
} end
To use Unmanaged Disks in a CAT resource, leave out the root_volume_type_uid attribute. A placement_group can optionally be specified, otherwise the default logic will be used.
placement_group "somestorageaccount" # Name of existing RightScale Placement Group (Microsoft Storage Account)
Full CAT Examples can be found in GitHub here:
- Server with Managed Disk Root Volume
- Server with Managed Disk Root and Data Volume
- Server with Managed Disk Root and Data Volume utilizing parameters
For further information about Managed Disks, see the Azure Managed Disks Overview from Microsoft.
Storage Accounts
The following applies to ARM Storage Accounts when used through RightScale:
- Whenever an instance is launched without explicitly specifying the Storage Account, RightScale
will use the Storage Account:
- that has the fewest number of instances associated with it AND that is in the instance’s Resource Group
OR - if there are no Storage Accounts with fewer than 20 instances, RightScale will generate a new Storage Account to use (see point 1 above). Auto-generated Storage Accounts will use the Standard_GRS Storage Account Type.
- that has the fewest number of instances associated with it AND that is in the instance’s Resource Group
- Storage Accounts in Azure Resource Manager are called Placement Groups (type: storage) in RightScale.
You will see them called
Storage Accounts
when in Azure-specific views, andPlacement Groups
in the API and generic views in RightScale.
Storage account containers with more than 10,000 blobs are not supported. See known limitations for more information
Storage Account Types
The following types of Storage Accounts can be created from the RightScale Cloud Management UI, via the API, or through Self-Service. When creating Placement Groups via the API or Self-Service, the account_type attribute within the cloud_specific_attributes hash would need to be set per the chart below:
| Azure - Storage Account Type | RightScale - account_type Value |
|---|---|
| Standard Locally-redundant storage (LRS) | Standard_LRS |
| Standard Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) | Standard_ZRS |
| Standard Geo-redundant storage (GRS) | Standard_GRS |
| Standard Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) | Standard_RAGRS |
| Premium Locally-redundant storage (LRS) | Premium_LRS |
Virtual Networks
Since Azure Virtual Networks require at least one subnet, when you create an Azure Virtual Network in RightScale, a subnet will automatically be created for that network with the same network CIDR. This subnet can be modified immediately thereafter to customize it, as required.
Network Interfaces
When choosing multiple subnets, the security group selected will be applied to both subnets selected. There is a limitation that prevents you from choosing different security groups per subnet.
Instances
Azure Resource Manager VMs map to RightScale Instances, the same as all other supported Clouds.
The Stopped (Allocated) VM status in Azure Resource Manager will map to a Running state in RightScale, as this is a billed state in Azure Resource Manager.
Terminate Behavior
- For VMs launched in a RightScale deployment,
terminateaction does: delete VM, Network interface and dynamically generated public ip (if there is one). - For VMs launched outside of a RightScale deployment,
terminateaction does: delete the resource group and all associated resources within it. - For VMs launched outside of a RightScale deployment but was RightLink-enabled,
terminateaction does: delete the resource group and all associated resources within it. - For VMs launched outside of a RightScale deployment but was later moved into a RightScale deployment, ,
terminateaction does: delete the resource group and all associated resources within it. - For VMs launched via the Azure Portal,
terminateaction does: delete only the VM